|
Venera 13
Venera 13 (russian: Венера-13 meaning Venus 13) was part of the Soviet Venera program meant to explore Venus. Venera 13 and 14 were identical spacecraft built to take advantage of the 1981 Venus launch opportunity. The probes were launched five days apart, with Venera 13 launching on 30 October 1981 at 06:04 UTC and Venera 14 launching on 4 November 1981 at 05:31 UTC. Both had an on-orbit dry mass of 760 kg. Venera 13 transmitted the first recording of actual sounds from another planet, including sounds of Venusian wind, the lander hitting the ground, pyrotechnic lens cap removal and its impact on regolith, and action of the regolith drilling apparatus. Design The descent lasted about an hour. Venera 13 landed at 03:57:21 UT at 7.5 S, 303 E, just east of the eastern extension of an elevated region known as Phoebe Regio. The area is composed of bedrock outcrops surrounded by dark, fine-grained soil. Cruise stage As the cruise stage flew by Venus, the bus acted as a da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never far from the Sun, either as morning star or evening star. Aside from the Sun and Moon, Venus is the brightest natural object in Earth's sky, capable of casting visible shadows on Earth at dark conditions and being visible to the naked eye in broad daylight. Venus is the second largest terrestrial object of the Solar System. It has a surface gravity slightly lower than on Earth and has a very weak induced magnetosphere. The atmosphere of Venus, mainly consists of carbon dioxide, and is the densest and hottest of the four terrestrial planets at the surface. With an atmospheric pressure at the planet's surface of about 92 times the sea level pressure of Earth and a mean temperature of , the carbon dioxide gas at Venus's surface is in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma-ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically shorter than those of X-rays. With frequency, frequencies above 30 exahertz (), it imparts the highest photon energy. Paul Ulrich Villard, Paul Villard, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation ''gamma rays'' based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; in 1900 he had already named two less penetrating types of decay radiation (discovered by Henri Becquerel) alpha particle, alpha rays and beta particle, beta rays in ascending order of penetrating power. Gamma rays from radioactive decay are in the energy range from a few kiloelectronvolts (keV) to approximately 8 megaelectronvolts (MeV), corres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penetrometer
A penetrometer is a device to test the strength of a material. Soil There are many types of penetrometer designed to be used on soil. They are usually round or cone shaped. The penetrometer is dropped on the test subject or pressed against it and the depth of the resulting hole is measured. The measurements find whether the soil is strong enough to build a road on. Scientists also use a penetrometer to measure how much moisture is in soil. Penetrometers are used by space probes such as the Cassini–Huygens probe, to measure the amount of moisture in soil on other planets. Penetrometers are furthermore used in glaciology to measure the strength and nature of materials underlying a glacier at its bed. A penetrometer is also used in longer professional cricket matches, to measure how the pitch is holding up over the course of a multi-day match. British horse racing courses have been required, since 2009, to report the readings obtained using a penetrometer designed by Cranfield U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometer
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated according ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photometer
A photometer is an instrument that measures the strength of electromagnetic radiation in the range from ultraviolet to infrared and including the visible spectrum. Most photometers convert light into an electric current using a photoresistor, photodiode, or photomultiplier. Photometers measure: *Illuminance *Irradiance *Light absorption * Scattering of light *Reflection of light *Fluorescence *Phosphorescence *Luminescence History Before electronic light sensitive elements were developed, photometry was done by estimation by the eye. The relative luminous flux of a source was compared with a standard source. The photometer is placed such that the illuminance from the source being investigated is equal to the standard source, as the human eye can judge equal illuminance. The relative luminous fluxes can then be calculated as the illuminance decreases proportionally to the inverse square of distance. A standard example of such a photometer consists of a piece of paper with an o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionization, ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluorescence, fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barometer
A barometer is a scientific instrument that is used to measure air pressure in a certain environment. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. Many measurements of air pressure are used within surface weather analysis to help find surface troughs, pressure systems and frontal boundaries. Barometers and pressure altimeters (the most basic and common type of altimeter) are essentially the same instrument, but used for different purposes. An altimeter is intended to be used at different levels matching the corresponding atmospheric pressure to the altitude, while a barometer is kept at the same level and measures subtle pressure changes caused by weather and elements of weather. The average atmospheric pressure on the earth's surface varies between 940 and 1040 hPa (mbar). The average atmospheric pressure at sea level is 1013 hPa (mbar). Etymology The word ''barometer'' is derived from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "weight", and (), meaning "measure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermometer
A thermometer is a device that temperature measurement, measures temperature or a temperature gradient (the degree of hotness or coldness of an object). A thermometer has two important elements: (1) a temperature sensor (e.g. the bulb of a mercury-in-glass thermometer or the pyrometric sensor in an infrared thermometer) in which some change occurs with a change in temperature; and (2) some means of converting this change into a numerical value (e.g. the visible scale that is marked on a mercury-in-glass thermometer or the digital readout on an infrared model). Thermometers are widely used in technology and industry to monitor processes, in meteorology, in medicine, and in scientific research. History While an individual thermometer is able to measure degrees of hotness, the readings on two thermometers cannot be compared unless they conform to an agreed scale. Today there is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. Internationally agreed temperature scales are designed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity, straight upwards (by definition) of g ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall (falling toward the center of the Earth at a rate of about 9.81 m/s2) will measure zero. Accelerometers have many uses in industry and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. Vibration in rotating machines is monitored by accelerometers. They are used in tablet computers and digital cameras so that images on screens are always displayed upright. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilise flight. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have almost the same chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos ( ἴσος "equal") and topos ( τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd in 1913 in a suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called its atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
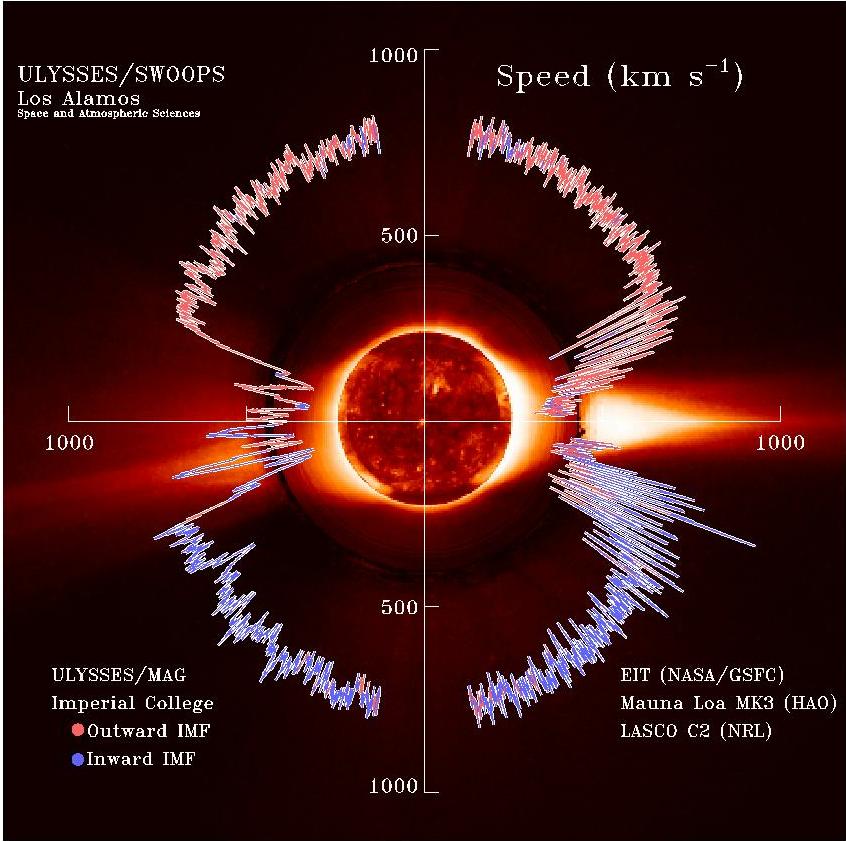
Solar Wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of materials found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei such as C, N, O, Ne, Mg, Si, S, and Fe. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as P, Ti, Cr, 54Fe and 56Fe, and 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface. At a distance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma-ray Burst
In gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are immensely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the most energetic and luminous electromagnetic events since the Big Bang. Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several hours. After an initial flash of gamma rays, a longer-lived "afterglow" is usually emitted at longer wavelengths (X-ray, ultraviolet, optical, infrared, microwave and radio). The intense radiation of most observed GRBs is thought to be released during a supernova or superluminous supernova as a high-mass star implodes to form a neutron star or a black hole. A subclass of GRBs appear to originate from the merger of binary neutron stars. The sources of most GRBs are billions of light years away from Earth, implying that the explosions are both extremely energetic (a typical burst releases as much energy in a few seconds as the Sun will in its entire 10-billion-year lifetime) and extremely rare (a few per galaxy per milli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)